Blockchain: The potential technology for the next generation business model
With all the industries that Blockchain is poised to disrupt, one of the side effects that will come of it is a change in internet business models. There are many different classifications of these decentralized applications powering business models, each with its own set of functions and use cases. The blockchain enables a decentralized ecosystem by which goods and services can be exchanged in a way that’s vastly different than what we’re used to. These ecosystems are referred to as dApps or DAO’s (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations). Blockchains are an example of a distributed computing system with high byzantine fault tolerance.
Definitions
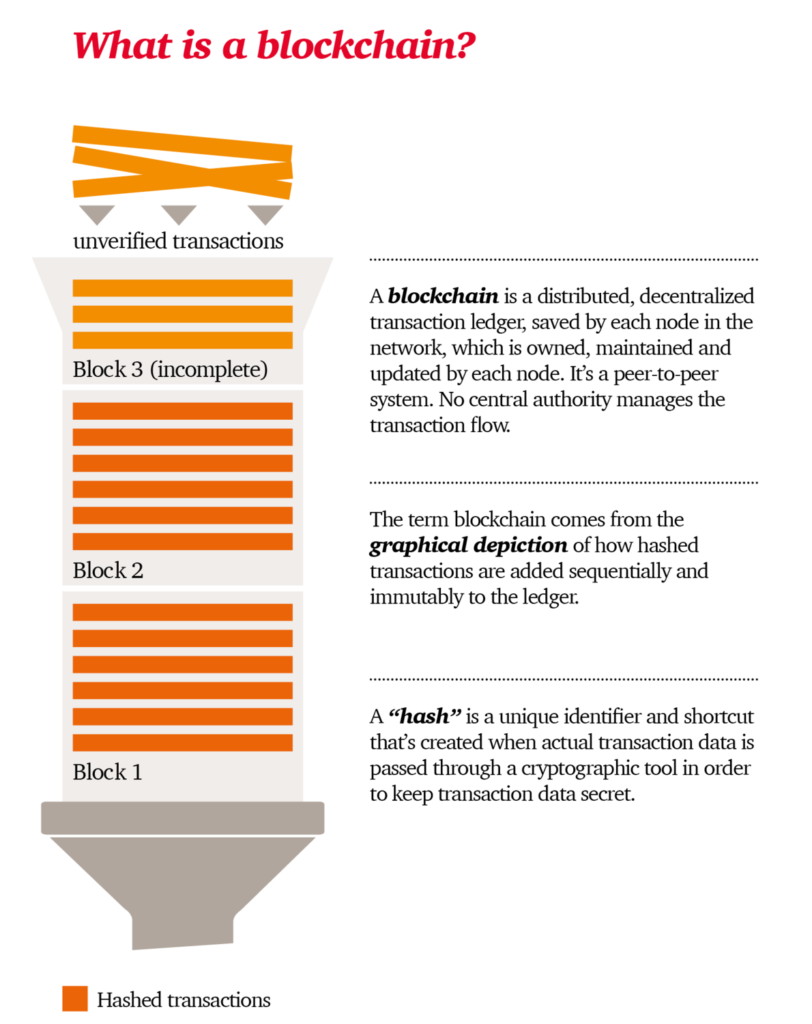
- A blockchain is a digital distributed transaction ledger, with identical copies maintained on multiple computer systems controlled by different entities.
- The blocks that make up the blockchain consist of: groups of transactions posted sequentially to the ledger – that is, added to the chain. Blockchain ledgers can be inspected publicly with block explorers, internet sites where you can see a transactions stream by entering a blockchain address.
- The blockchain database is shared by all network nodes, updated by miners, monitored by everyone, and owned and controlled by no one.
- Technology that permanently records transactions in a way that cannot be later erased but can only be sequentially updated, in essence keeping a never-ending historical trail.
- Blockchain is a disruptive technology that uses a distributed messaging protocol to create a shared ledger between trading counterparties to validate transactions.
In 1978, Leslie Lamport is one of the founding fathers of distributed computing and distributed algorithms. “A distributed system consists of a collection of distinct processes which are spatially separated, and which communicate with each other by exchanging messages. A network of interconnected computers such as the ARPANET is a distributed system.” The key requirement in the development of distributed computing is that a system made up of distributed processes has to be able to keep functioning, even when one or several of its components have ceased to (reliably) contribute to the functioning of the system as a whole. A distributed system can function reliably by using time as a fundamental part of its reliability. As a whole, the system can only function reliably on a permanent basis when the majority of separate components of the system maintain consensus with respect to the functioning of the system as a whole. It is therefore key for a distributed system that all components involved keep a ledger of how and with whom they have performed transactions by exchanging and sharing data and information. All components must have access to information about transactions logged in the distributed ledgers, which are intended to provide an overall view of all approved transactions.
Mr. Lamport develops an algorithm that lays the foundation for reliable consensus between systems that are separated in terms of time and space. The essential idea in the solution they come up with is that to establish consensus there have to be at least three plus one component and mutual exchange of qualified messages between them. A protocol to this consensus principle was added to regulate the voting that is needed to achieve consensus between the various components within a system. This protocol, which is also known as the Paxos algorithm, addresses things such as how to handle the voting between the various components, how to record the results of the voting between the components in central and decentralized ledgers, and how to guarantee the consistency of recorded information.
After Lamport, the most widely known application of this technology so far is attributed to Satoshi Nakamoto Bitcoin.
The blockchain has several features which financial services companies find compelling.
- Decentralized (doesn’t have a single point of failure)
- Secure (utilizing cryptography to validate every transaction)
- Immutable history (write-once, spend-only attribute of the ledger)
- Efficient (exchange of information is fast and easy)
- Transparent (everything is documented)
It is the robustness and relative simplicity of the Bitcoin blockchain that has sparked the interest of similar technology to be applied everywhere.
Opportunities
Some of the innovative use cases of blockchain that are being explored are
- KYC/AML data sharing,
- Trade surveillance,
- Regulatory reporting,
- Collateral management,
- Trading,
- Settlement and clearing
- Value calculation
- Currency exchange,
- Data storage in the cloud
- Contracts
- Add participants over time
- Disintermediation and decentralization of all transactions of any type between all parties on a global basis.
- Decentralized ledgers that enable a transparent structure of recorded transactions.
- Computers, smartphones, sensors, and devices such as smart TVs, fridges, and cars can thus be interconnected through software and distributed algorithms that ensure consensus in transactions between these nodes
- Domain Name System with a blockchain for Internet names
- Blockchain as Notary services
- Blockchain as a crowdfunding platform
- Blockchain-based browser level Security certificate authorities (Alternative to TSL/SSL)
- Distributed email service
- Distributed social network
- Verify identities & Trustworthy endorsement
- On-demand code execution on invocation of app or web page
- Massive server farms could be replaced by massive distributed peer-to-peer networks: open-source, encrypted end-to-end, and orchestrated in part by blockchains
- Smart Contract, assets, communities, cities, or Proof of authorship or ownership
- Blockchain as a service
- Energy or grant distribution
- Energy Efficiency
- Internet of things
- Voting system
- Multi-party aggregation
- Provenance tracking
- Custodian services
- Inter-organization record keeping
- Predictive platforms and online gaming
- Digitization of documents & contracts
- Digital security trading
- Luxury and medical goods authentication
- Government services
- Currency exchange and remittance
- Collaborative transport or Ridesharing
- Decentralized market places
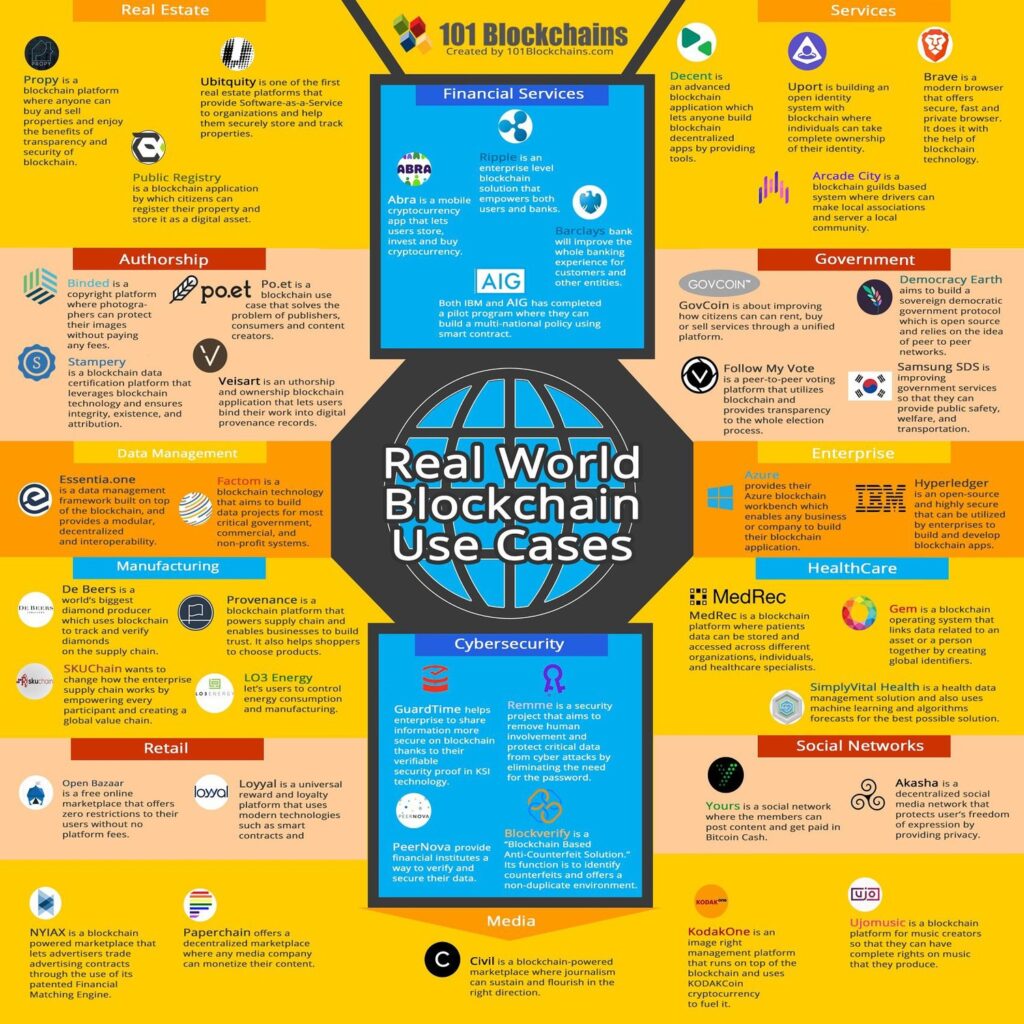
Some of the specialized use cases popular in the financial service sector are
- Currency exchange,
- Supply chain management,
- Trade execution and settlement,
- Remittance
- Peer-to-peer transfers (lending, borrowing, payments)
- Micro-payments,
- Asset registration,
- Correspondent banking and regulatory reporting
Approach
- Evaluate Proof of concept/work to explore possible potentials of existing Blockchain technologies such as
- Bitcoin
- Ethereum
- Stratis
- Open source projects
- https://www.openchain.org/
- https://www.hyperledger.org
Most players in the race are exploring various use cases as they ride the hype cycle called Blockchain.
“In five to 10 years the financial services industry will be unrecognizable, they move value, they store value, they lend value, they exchange values, they account for value, they attest to value: every one of those could be disrupted very profoundly by this technology.” : Don Tapscott
- http://www.ibm.com/blockchain/business-use-cases.html
- https://letstalkpayments.com/an-overview-of-blockchain-technology/
- http://www.digitalistmag.com/digital-economy/2016/04/18/blockchain-good-bad-business-case-04145447
- http://bravenewcoin.com/news/moodys-new-report-identifies-25-top-blockchain-use-cases-from-a-list-of-120/
- http://www.i-cio.com/big-thinkers/don-tapscott/item/why-blockchains-will-rewrite-business-models-and-revolutionize-industries
Conclusion
- Blockchain concept and technology is still evolving
- Pilots and tests being run to explore all round (360 degrees) potential of Blockchain technology
- The banking, financial services & insurance sector is wary of security issues due to various breaches to date on various blockchain implementations including bitcoin and other crypto-currencies.
- Blockchain is receiving unprecedented attention due to the first successful implementation of distributed computing based upon Decentralized architecture.
- The Tech industry has the worst track record of only under 20% deliveries leading to production, unlike other industries. Was it the centralized architecture of “Stacks” reason behind it?
- Looking back to connect dots (considering all analysis and observations, it is more logical to find why blockchain is now considered as panacea for everything in tech space and now they want to rewrite everything including the internet.
- Consulting, POCs, Testing, and consuming technologies from early adopters (IBM, Microsoft, TCS, etc.) could be some of the “low hanging fruits”.
- Else some of these highly-rated use cases could be considered for investment to keep ahead in this “new gold rush”. These and new generation business cases /use cases could be delivered by aggregating Blockchain and currently trending technologies such as AI, ML, Data Science, NLP/Cognitive science, Context-aware computing, Mesh, cloud, IoT, mobility, etc.
Read our blog articles
Digital Process Automation
How can we help you?
Contact us for Free Consultation on "How to adopt digital technologies to transform your business?




